![]()
where v1 and v2 are the input volumes, w1 and w2 are floating point weights, and (OP) is the pointwise function for combining the two weighted input volumes. The output goes into v1.
Among the functions available are (by toggling the menu parameter ``function = '' as shown below):
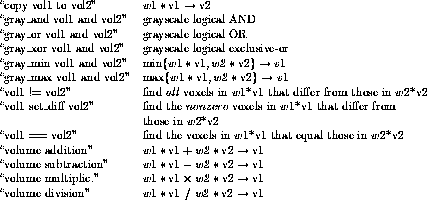
All operations are rounded to 8-bit arithmetic.
The functions ``volume addition'' and ``volume multiplic.'' set the result to 255 if the computed result is > 255.
The function ``volume subtraction'' sets the output to 0 if
![]() v2
v2 ![]() v1.
v1.
The function ``volume division'' sets the output to 255 if
the product ![]() v2 = 0.
v2 = 0.
The functions gray_and, gray_or, and gray_xor work as the
corresponding logical operations and, or, and exclusive-or on
grayscale data. Any voxel having grayscale value >
0 is treated logically as a 1; only 0 voxels are treated as logical
0's. For each pair of corresponding voxels from the two input
volumes, the gray_and, gray_or, and gray_xor first check to see
if the logical condition is passed; if it is, the output assumes
the maximum grayscale value of the two voxels. For example, if
voxel ![]() assumes the values v1(x,y,z)
= 100 in v1 and v2(x,y,z) = 50 in v2 and w1 2.0
and w2 = 0.5, then the gray_and, gray_or, and gray_xor
output the following values:
assumes the values v1(x,y,z)
= 100 in v1 and v2(x,y,z) = 50 in v2 and w1 2.0
and w2 = 0.5, then the gray_and, gray_or, and gray_xor
output the following values:
![]()
if instead v1(x,y,z) = 0 (and all else the same), then
![]()
function = copy vol1 to vol2The parameter ``function = '' should be toggled to the desired function.
* volume1 weight = 1.000
* volume2 weight = 1.000
* first volume = 0
* second volume = 0
* copy output to vol # = 1
*